However these theories do not explain the Meissner effect: the process by which a magnetic field is expelled from the interior of a metal undergoing a transition to the superconducting state. Nor do they provide a dynamical explanation of the London moment generation.
The following papers explain why BCS-London theory can't explain the
Meissner effect
and offer an explanation for it:
superconductors expel magnetic field because they expel
negative charge
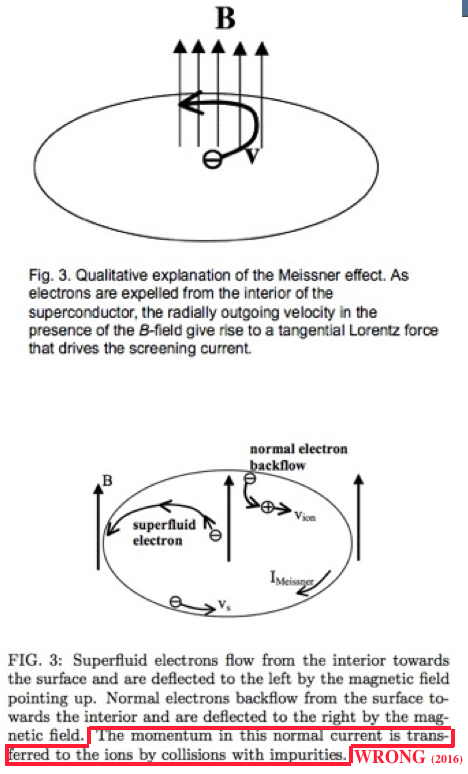
[1] Consequences of charge imbalance in superconductors within the theory of hole superconductivity , cond-mat/0012517, Phys.Lett.A 281, 44 (2001)
[2] Superconductors as giant atoms predicted by the theory of hole superconductivity , cond-mat/0301611 , Phys.Lett.A 309, 457 (2003).
[3] The Lorentz force and superconductivity , cond-mat/0305542, Phys.Lett.A 315, 474 (2003).
[4] Superconductors as giant atoms: qualitative aspects , cond-mat/0305574 (2003), AIP Conf. Proc. 695(1) 21 (17 Dec 2003).
[5] Charge expulsion and electric field in superconductors , cond-mat/0308604, Phys.Rev. B 68, 184502 (2003).
[6] Do superconductors violate Lenz's law? Body rotation under field cooling and theoretical implications, Phys.Lett. A366, 615 (2007).
[7] Spin Meissner Effect in Superconductors and the Origin of the Meissner Effect , arXiv:0710.0876 (2007), Europhys. Lett. 81, 67003 (2008).
[8] Electrodynamics of spin currents in superconductors , arXiv:0803.1198 (2008), Ann. Phys. (Berlin) 17, 380 (2008).
[9] The missing angular momentum of superconductors , arXiv:0803.2054, (2008), J. Phys. Cond. Matt. 20, 235233 (2008).
[10] BCS theory of superconductivity: it is time to question its validity, Physica Scripta 80 (2009) 035702.
[11] Charge expulsion, Spin Meissner effect, and charge inhomogeneity in superconductors , arXiv:0810.5127, (2008), Journal of Superconductivity and Novel Magnetism 22, 131 (2009).
[12] Explanation of the Meissner Effect and Prediction of a Spin Meissner Effect in Low and High $T_c$ Superconductors, Physica C 470, S955 (2010).
[13] Electromotive forces and the Meissner effect puzzle, Journal of Superconductivity and Novel Magnetism 23, 309 (2010) dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10948-009-0531-4.
[14] Kinetic energy driven superconductivity, the origin of the Meissner effect, and the reductionist frontier, arXiv:1103.3912 (2011), Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 25, 1173 (2011).
[15] Meissner effect, Spin Meissner effect and charge expulsion in superconductors , arXiv:1106.5311 (2011), J Supercond Nov Magn 26, 2239 (2013).
[16] Correcting 100 years of misunderstanding: electric fields in superconductors, hole superconductivity, and the Meissner effect, arXiv:1202.1851, J Supercond Nov Magn 25, 1357 (2012).
[17]
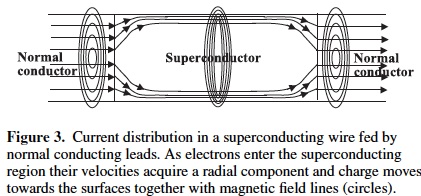 The origin of the Meissner effect in new and old superconductors
,
arXiv:1201.0139 (2011), Physica Scripta 85, 035704 (2012).
The origin of the Meissner effect in new and old superconductors
,
arXiv:1201.0139 (2011), Physica Scripta 85, 035704 (2012).
[18] Kinetic energy driven superfluidity and superconductivity and the origin of the Meissner effect, arXiv:1210.1578 (2012), Physica C 493, 18 (2013) .
[19] Dynamic Hubbard model: kinetic energy driven charge expulsion, charge inhomogeneity, hole superconductivity, and Meissner effect, arXiv:1302.4178 (2013), Physica Scripta 88, 035704 (2013).
[20] The London moment: what a rotating superconductor reveals about superconductivity, arXiv:1310.3834 (2013), Physica Scripta 89, 015806 (2014).
[21] Dynamics of the normal-superconductor phase transition and the puzzle of the Meissner effect , arxiv: 1504.05190 (2015), Annals of Physics 362, 1 (2015).
[22] On the dynamics of the Meissner effect, arxiv: 1508.03307 (2015), Physica Scripta 91, 035801 (2016).
[23]
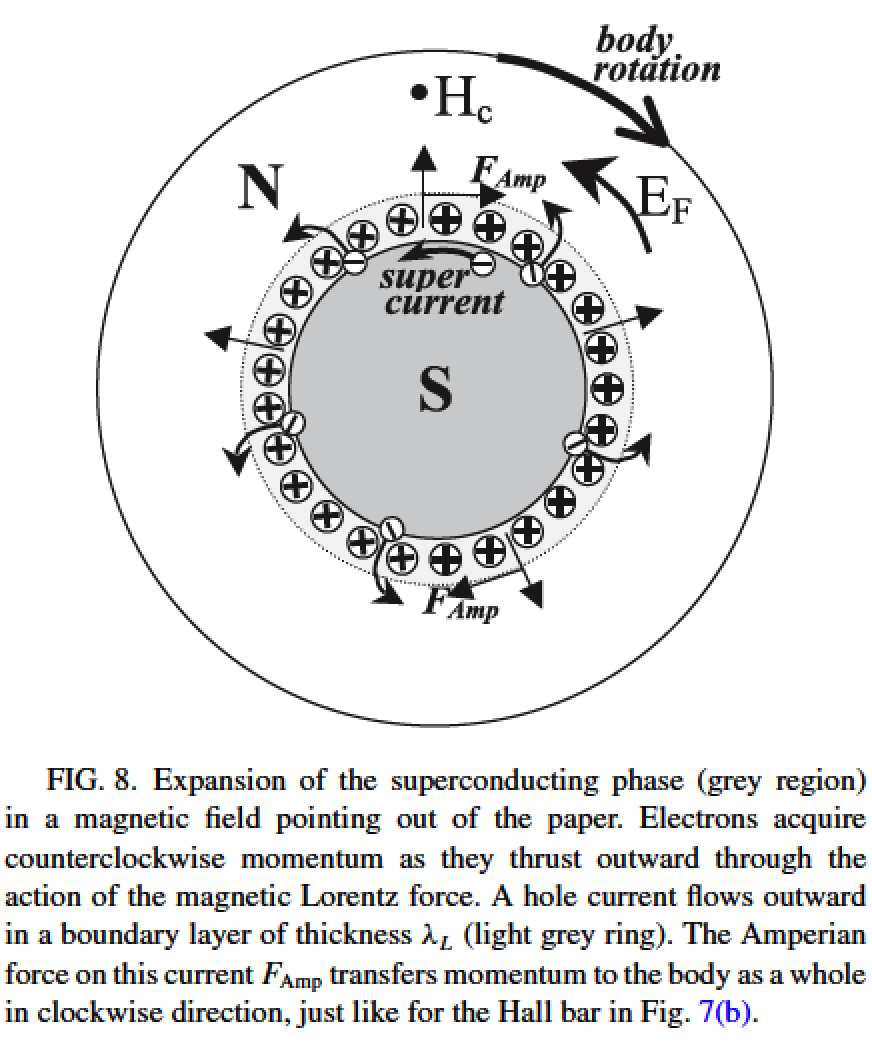 The disappearing momentum of the supercurrent in the superconductor to normal phase transformation,
arxiv:1604.03565 (2016),
Europhys. Lett. 114, 57001 (2016)
.
The disappearing momentum of the supercurrent in the superconductor to normal phase transformation,
arxiv:1604.03565 (2016),
Europhys. Lett. 114, 57001 (2016)
.
[24] On the reversibitity of the Meissner effect and the angular momentum puzzle, arXiv:1604.07443 (2016), Annals of Physics 373, 230 (2016) .
[25] Corrigendum on "On the dynamics of the Meissner effect", arXiv:1609.06299 (2016), Physica Scripta 91, 099501 (2016).
[26] Momentum of superconducting electrons and the explanation of the Meissner effect, arXiv:1609.08451 (2016), Phys. Rev. B 95, 014503 (2017).
[27] Why only hole conductors can be superconductors, Proc. SPIE 10105, Oxide-based Materials and Devices VIII, 101051V (March 7, 2017), arXiv:1703.09777.
[28] Entropy generation and momentum transfer in the superconductor-normal and normal-superconductor phase transformations and the consistency of the conventional theory of superconductivity, arxiv: 1703.04404 (2017), Int. J. Mod. Phys. B Vol. 32, 1850158 (2018).
[29] Spinning Superconductors and Ferromagnets, Acta Physica Polonica A 133, 350 (2018)
[30] Moment of inertia of superconductors, arXiv:1808.02857 (2018), Physics Letters A 383, 83 (2019)
[31] Defying inertia: how rotating superconductors generate magnetic fields, arXiv:1812.06780 (2018), Annalen der Physik (2019).
[32] Alfven-like waves along normal-superconductor phase boundaries , arXiv:1906.03083 (2019), Physica C 564, 42 (2019)
[33] Thermodynamic inconsistency of the conventional theory of superconductivity , arXiv:1907.11273 (2019), Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 34, 2050175 (2020).
[34] Superconducting materials: the whole story, arXiv:1908.04419 (2019), J Supercond Nov Magn 33, 61–68 (2020).
[35] How Alfven's theorem explains the Meissner effect, arXiv:1909.11443 (2019), Mod. Phys. Lett. B 34, 2050300 (2020).
[36] Inconsistency of the conventional theory of superconductivity, arXiv:1909.12786 (2019), EPL 130, 17006 (2020).
[37] Joule heating in the normal-superconductor phase transition in a magnetic field, arXiv:2001.07509 (2020), Physica C 576, 1353687 (2020).
[38] Magnetic flux expulsion in a superconducting wire, arXiv:2106.00262 (2021), Physics Letters A 413, 127592 (2021).
[39] Superconductivity, what the H? the emperor has no clothes, International Journal of Modern Physics B 2430001 (2024), APS Forum on Physics and Society Newsletter, January 2020, p. 4-9 .
[40] On Thermal and Electrodynamic Aspects of the Superconductive Transition Process, Materials 2024, 17, 254 .
[41] Does the Meissner effect violate the second law of thermodynamics?, Physica C 1354618 (2024).
[42] Does the Meissner effect require radial charge flow?, Physica C 633 1354724 (2025).
[43] How do supercurrents die down when a superconductor goes normal?, Physica C 635, 1354747 (2025).
[44] What holes in superconductors reveal about superconductivity, arXiv:2506.07361 (2025).